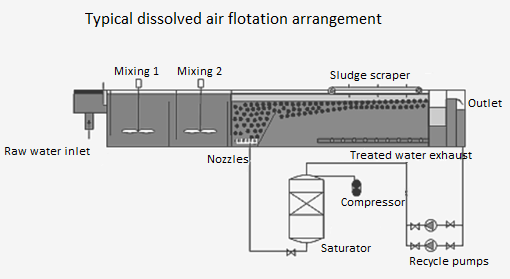
Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF) is a separation process that is designed as a first separation step in the treatment of drinking water or in the treatment of various types of wastewaters. Suspended substances (flakes, particles, organisms) combine with air microbubbles in the contact zone and are then brought to the surface in the separation zone where they form a floating layer of sludge foam which is removed hydraulically or mechanically. The upward velocities of the aggregates thus formed are one to two orders of magnitude higher than the original sedimentation velocities of these flakes, which allows operation at the high surface loading of flotation compared to sedimentation. Thus, in contrast to sedimentation, the purpose is not to create large, fast-sedimented flakes, but rather smaller flakes that will rise to the surface upon contact with air microbubbles. Dissolved air flotation is particularly suitable for treating water with higher concentrations of organic matter, colour and micro-organisms (algae, cyanobacteria). Conversely, it has some limitations in terms of turbidity of raw water. A value of < 100 NTU/FNU is recommended.
Main characteristic/Customer benefits
- High separation efficiency, even contaminants with low sedimentation rates
- Low doses of chemicals
- Low load the subsequent stage
- Sludge production of high dry solids (0.5-6 %)